Herniated Disc: Symptoms and Treatments
 The backbone has two important functions. First, it is part of the skeleton:
the frame of bones that gives the body its shape. Lastly, it supports and
protects the spinal cord from damage by external forces. The spinal cord is part
of the delicate nervous system that relays messages from the brain to other
parts of the body. These important functions have earned the backbone three
other names: vertebral column, spinal column, and spine. Twenty-four separate
small bones build up the backbone. It stretches from the skull to the pelvic
bone. The hollow in the bones forms the spinal canal through which the spinal
cord passes. Circular pads of cartilage, usually called intervertebral discs,
separate the ends of neighboring bones. They prevent the ends of the bones from
rubbing against each other. Therefore, they protect the bones from fast wear and
tear. Furthermore, they cushion the backbone from shock. The outer cover of the
disc is a thin tough cartilage whereas the inner part consists of a jelly like
substance. If you engage in activities that subject the disc to high pressure,
the cartilage can rupture and enable the jelly to protrude into the spinal
canal. A herniated disc is a disc with a ruptured cartilage and protruding inner
substance. This article describes herniated discs: symptoms, causes, diagnosis,
treatment, and prevention. The backbone has two important functions. First, it is part of the skeleton:
the frame of bones that gives the body its shape. Lastly, it supports and
protects the spinal cord from damage by external forces. The spinal cord is part
of the delicate nervous system that relays messages from the brain to other
parts of the body. These important functions have earned the backbone three
other names: vertebral column, spinal column, and spine. Twenty-four separate
small bones build up the backbone. It stretches from the skull to the pelvic
bone. The hollow in the bones forms the spinal canal through which the spinal
cord passes. Circular pads of cartilage, usually called intervertebral discs,
separate the ends of neighboring bones. They prevent the ends of the bones from
rubbing against each other. Therefore, they protect the bones from fast wear and
tear. Furthermore, they cushion the backbone from shock. The outer cover of the
disc is a thin tough cartilage whereas the inner part consists of a jelly like
substance. If you engage in activities that subject the disc to high pressure,
the cartilage can rupture and enable the jelly to protrude into the spinal
canal. A herniated disc is a disc with a ruptured cartilage and protruding inner
substance. This article describes herniated discs: symptoms, causes, diagnosis,
treatment, and prevention.
Symptoms of Herniated Disc
A herniated disc causes symptoms if its protrusion compresses the spinal cord or
a nerve root. The symptoms depend on its location, how large the protrusion is,
and the nerve root it compresses. It can compress no nerve, a single nerve root,
or the entire spinal cord. First, there can be little or no discomfort if the
protrusion is small and it does not affect any nerve. Second, a slight
compression on a nerve root can cause numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness
along the areas it innervates.
Third, a large protrusion can subject a nerve root or the spinal to very high
compression and cause persistent unbearable pain and paralysis in the lower
back, neck and areas the affected nerves innervate.
Fourth, a herniated disc in the lumber region can affect the sciatic nerve,
which innervates the buttocks and legs. Consequently, the patient can experience
the symptoms in the buttocks, a condition called scartica. Furthermore, if the
herniated disc is the one that separates the lumber vertebrae L3 and L4 or L4
and L5, a male patient can suffer erectile dysfunction.
Lastly, the patient usually experiences the symptoms on one side of the body.
However, a high compression of the spinal cord or the cauda equina nerve can
cause the symptoms in both sides of the body. The cauda equina nerve is in the
lumbar region. High compression on this nerve can permanently damage it and
cause paralysis: cauda equina syndrome.
Causes of Herniated Disc
The main causes of herniated discs are shock and wear and tear. First, a sudden
shock on the backbone can cause disc rupture. For instance, the backbone can be
subjected to sudden shock in a motor vehicle accident or fall on the stairs.
Furthermore, lifting heavy objects can cause a herniated disc.
Second, activities that subject people to constant squatting or sitting cause
most cases of herniated discs. With time, these activities cause high wear and
tear on the outer cover of the discs. Worn out discs easily rupture when
subjected to trauma such as when lifting a heavy object. Chronic back tiredness
and minor back pain are symptoms of general wear and tear of the discs.
The internal pressure on the disc is even when you are lying down or
standing. However, the disc internal pressure is disproportionate when you are
bending: the side of the disc that faces the stomach gets higher compression
than the opposite side. This pressure can build up to very high values: up to
300 psi. Therefore, disc rupture usually occurs on the side facing the stomach.
Such a rupture usually occurs when bending forward or sitting. The rupture
occurs when high pressure from bending bears on the outer cartilage already
thinned from wear and tear. Lastly, some people inherit the risk of developing
herniated discs.
Location of a Herniated Disc
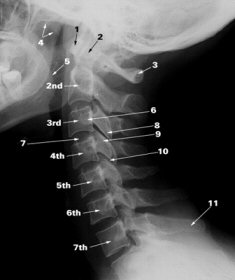 The backbone has three distinct sections. Each section comprises individual
bones called vertebrae. First, the cervical spine is the neck section. It has
seven vertebrae designated as C1 to C7. C1 is the vertebra attached to the
skull. Second, the thoracic spine is the section in the thorax. It has twelve
vertebrae designated as T1 to T12. T1 is the top one attached to C7. Lastly, the
lumbar spine is the section in the lower back. It has five vertebrae designated
as L1 to L5. L1 is the top one attached to T12. Furthermore, part of the pelvic
bone called the sacrum is below the lumber. It has five individual bones fused
together and usually designated as S1 to S5. S1 is the top one attached to L5. The backbone has three distinct sections. Each section comprises individual
bones called vertebrae. First, the cervical spine is the neck section. It has
seven vertebrae designated as C1 to C7. C1 is the vertebra attached to the
skull. Second, the thoracic spine is the section in the thorax. It has twelve
vertebrae designated as T1 to T12. T1 is the top one attached to C7. Lastly, the
lumbar spine is the section in the lower back. It has five vertebrae designated
as L1 to L5. L1 is the top one attached to T12. Furthermore, part of the pelvic
bone called the sacrum is below the lumber. It has five individual bones fused
together and usually designated as S1 to S5. S1 is the top one attached to L5.
Most cases of herniated discs involve discs in the lumbar region: ninety five
percent of cases. They usually involve the discs between L5-S1 and L4-L5. A
herniation of either or both of these discs causes the symptoms in the toe,
genital area, anal area, thigh, buttocks, and lower back. It usually affects the
sciatic nerve and can lead to a condition called sciatica. Furthermore, it can
affect the perineal nerve, which innervates the genital and anal areas. Besides,
it can affect the femoral nerve and cause pain, burning sensation, tingling,
and/or numbness in one or both feet, legs, and hips.
The second most common cases involve discs in the cervical region especially
those between C5-C6 and C6-C7. A herniation of either or both of these discs can
cause the symptoms in the hand, arm, shoulder, scapula, shoulder girdle, neck,
and skull. It usually affects the brachial plexus and cervical plexus nerves.
Cases of herniated disc in the thorax region are few: only about four percent.
Diagnosis of Herniated Disc
It can take some time before doctors diagnose a herniated disc because initially
the patient complains of pain in remote areas of the body such as feet, knees,
or thighs. Apart from pain, the patient can experience weak reflexes, numbness,
paresthesia, tingling, paralysis, and muscle weakness.
The doctor can perform physical examination to diagnose a herniated disc. The
type of examination he performs depends on the symptoms and health history of
the patient. Furthermore, he can perform tests to confirm herniated disc and
rule out other health problems with similar symptoms. The tests can also
determine the best treatment option. The doctor can use one or a combination of
the following seven physical examination methods.
First, the Straight Leg Raise (SLR) is a simple test for herniated disc.
However, it is a very sensitive test to confirm or rule out herniated disc,
sciatica and low back pain. The patient lies on the back and raises one leg
without bending the knee. If the patient feels pain, the doctor repeats the test
while flexing the leg about the pelvis. The test is positive if the leg raise
with flexing does not cause pain. A positive SLR confirms the presence of
herniated disc, sciatica or low back pain. .
Second, x-ray cannot produce images of soft tissues such as nerves, muscles,
and discs. However, it can show fractures, infections, and tumors. Therefore, it
is an inexpensive method to begin with because it helps rule out these problems
and strengthen suspicion for herniated disc.
Third, Computed Tomography scan (CT or CAT scan) uses the computer to
interpret x-ray images. It can show the size and shape of the spinal canal, the
spine, and objects around the spine including soft tissues. However, it cannot
confirm a herniated disc. It helps rule out other problems.
Fourth, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses computer technology and
powerful magnets to produce three-dimensional images. It produces clearer images
of soft tissues than CAT. It can show nerve roots and their vicinity, tumors,
and spinal cord. Therefore, doctors use it confirm the presence of a herniated
disc especially if the magnetic field used has high strength. T2-weighted images
can produce a clear image of the jelly substance from the disc protruding in the
spinal canal.
Fifth, Myelogram consists of taking x-ray images after injecting a contrast
material into the spinal canal. Doctors use it together with CT scan. It can
clearly show a herniated disc and other structures such as bone spurs and
tumors. Sixth, Electromyogram and Nerve Conduction Studies (EMG/NCS) measures
electrical impulse in muscle tissues, peripheral nerves, and nerve roots. The
test can show nerve damage, healing nerves, and compressed nerves. The doctor
can use it to confirm the location of a herniated disc.
Lastly, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) test can show if and where
the spinal cord is compressed. Furthermore, it can show how severe the
compression is. It consists of measuring the time a nerve impulse takes to
travel from brain to the end of lumbar, thoracic, or cervical spinal cord. To
perform the test, the doctor stimulates the impulse in the brain with a
high-intensity magnetic field. He passes the magnetic field into the brain very
briefly. Therefore, it is noninvasive. TMS can enable the doctor to confirm
spinal cord compression, location of the compression, progress of treatment, and
cause of the compression.
Treatment of Herniated Disc
 If given time, herniated discs usually heal without much intervention.
However, the patient should avoid activities that can aggravate the herniation.
Therefore, doctors usually recommend rest. During the period of rest, the doctor
can prescribe painkillers and anti inflammation drugs to help manage the pain.
Furthermore, he can recommend non-medical approaches such as gentle exercise,
rehabilitation, anti-depressants, and physical therapy. If given time, herniated discs usually heal without much intervention.
However, the patient should avoid activities that can aggravate the herniation.
Therefore, doctors usually recommend rest. During the period of rest, the doctor
can prescribe painkillers and anti inflammation drugs to help manage the pain.
Furthermore, he can recommend non-medical approaches such as gentle exercise,
rehabilitation, anti-depressants, and physical therapy.
This period of rest usually frustrates patients because of the persistent
unbearable pain, taking a lot of pain management medicine, inability to perform
normal duties and feeling of neglect. The doctor monitors the healing progress
during the rest period that may take up to six months. If these conservative
measures do not relieve pain, the doctor can perform surgery to correct the
herniated disc, as a last resort.
The doctor can recommend conservative treatment methods depending on the
condition of the patient. They usually consider severity of both the pain and
injury. The severity of the injury can be minor and result in minor discomfort.
However, a major injury can cause unbearable pain and restrict movement. An MRI
test can show the severity of the injury.
You can use the following five conservative treatment methods if diagnosed
with a herniated disc. Your doctor can advise which methods can work for your
case. First, spend most of your time lying down: avoid sitting and bending.
Lying down gives your body the best opportunity to heal. However, avoid the bed
and couch. Instead, use a duvet on the floor because it offers maximum support
for your body. You should lie on your back most of the time to keep your spine
straight. When lying on your back, you should bend your knees to raise your legs
slightly to reduce pressure on your spine. Therefore, place some pillows under
your knees.
Furthermore, you can lie on your side with pillows between your legs.
However, avoid lying on your stomach because it makes the joints stiffen.
Second, you should perform gentle exercises. Inactivity can make the joints
accumulate fluid and expand. This makes them become more painful. Take a stroll
several times during the day. You can also perform slow push-ups. Furthermore,
you can swim. Swimming provides gentle exercise because the water supports your
body.
Third, do not use the bath: use a shower instead. In the bath, you cannot
keep your backbone straight. Therefore, the bath helps aggravate the pain.
Fourth, try to keep your mind off the pain, which seems to intensify during the
day. You can read or watch movies while lying on your back. The pain will become
unbearable if you idle about feeling sorry for yourself. Lastly, use the pain
management drugs prescribed by the doctor and report to him if they do not work
for you. A combination of painkillers and anti-inflammatory can help manage the
pain. For instance, you can take ibuprofen and tramadol. If the pain persists
for more than six months, the doctor can decide to perform surgery.
Surgery - Doctors resort to surgery when the conservative methods of
treatment fail, for an emergency case such as cauda equina syndrome, or when the
patient has significant impaired functionality of the nervous system. The doctor
can perform the surgery to remove part of the disc and release the compressed
nerve.
Prevention of Herniated Disc
 Individuals and health authorities can take the following measures to help
prevent cases of herniated discs. First, authorities should educate the public
and create awareness on the problems and prevention of herniated disc. Second,
you should avoid lifting heavy weights. Do not lift weights beyond your
capability. Individuals and health authorities can take the following measures to help
prevent cases of herniated discs. First, authorities should educate the public
and create awareness on the problems and prevention of herniated disc. Second,
you should avoid lifting heavy weights. Do not lift weights beyond your
capability.
Third, you should maintain proper alignment and posture of the backbone to
avoid degradation of the discs. Poor posture causes wear and tear on the discs.
Bending increases the risk of herniated disc. Furthermore, if your work involves
long hours of sitting, then you should use a proper seat and perform exercises
that help firm your back muscles.
Fourth, you should avoid overworking yourself. Furthermore, you should give
your body some rest after a strenuous activity. Do not work until you feel
fatigued. Symptoms of fatigue include loss of the deep stomach muscles, shaking,
burning sensation in the muscles and poor coordination. If you engage in
activities that subject the body to high stress, such as weightlifting, you
should use barbells to strengthen the muscles. Furthermore, you should use
lumbar sacral support belts to confine movement of the backbone during lifting.
Lastly, you should perform exercises that help firm your back muscles. Such
exercises include floor bridges, transverse abdominal bracing, and prone
press-ups. Abdominal bracing exercises can help prevent disc and joint injury.
Diseases & Conditions
Top Lists:
Top 10 Most Common Genetic Disorders
Top 15 Most Disturbing Skin Conditions
10 Unusual Phobias
Informational:
Diverticular Disease and Diverticulitis
What is Turner Syndrome and Why Does it Affect Only Females?
Alice in Wonderland Syndrome and How to Treat the Symptoms
Herniated Disc: Symptoms and Treatments
Pinch Nerve: The Cause of Remote Pain
Dealing With a Child Who Has a Fever
How Unhealthy Diet Could Trigger Inflammatory Arthritis
Phobias: Understanding How They Develop and Treatments
Depression Facts, Symptoms & Treatment
Earaches - Causes and Treatments
Symptoms of Borderline Personality Disorder and How to Deal with It
Seasonal Affective Disorder: Does Light Therapy Help?
What Really Causes Dandruff and How Can You Treat the Symptoms
Treating Plantar Fasciitis or Heel and Arch Pain
Symptoms and Treatments of Aplastic Anemia
Using Sclerotherapy to Get Rid of Varicose Veins
Are the Side Effects of HGH Supplements Worth It?
ADD/ADHD Symptoms and Treatment
What are the Options for Hair Loss Treatments
Options for Frontal Hair Loss Treatment |