15 Remarkable Facts About Bacteria
Bacteria are often considered as bad organisms because they are often associated
with illness and disease. However, these one-celled microorganisms are not just
pathogenic in nature. Dating back to the time before the dinosaurs,
all types of bacteria were found just about everywhere. Microscopically sized, bacteria
can be may are shaped in spirals, rods, and orbs.
While bacteria can cause infections or illness, they can be beneficial to
humans too. Good bacteria are helpful to digestive health and immune system
functionality. Foods like yogurt include the good kind of bacteria
to keep people regular, commonly known as probiotics. Good digestive health is maintained by
healthy probiotics and the quantities those tiny bacteria inside of someone.
Those people who get healthy probiotics regularly are more likely to
live much more mentally healthy, balanced lives as most serotonin is produced in
the GI tract or "gut". Bacteria is used for food preservation, enhances the
virility of crop soil, and bacteria even helps to eliminate solid waste.

Adaptable to a variety of environments, bacteria can act as contagions as
well. For example, E.coli bacteria is associated with the bacteria that are
found in feces. Bacteria also causes such diseases as the flu and common cold –
both produce symptoms like coughing, tearing or running eyes, and a runny nose.
Probiotic Cycle in Body
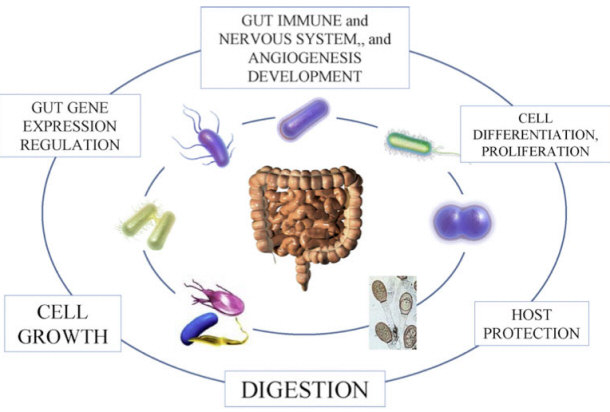
Bacteria are both interesting and fascinating organism because of their
adaptability, longevity, and microscopic complexity. The following are fifteen
facts about bacteria demonstrating how contact with them is an absolutely
unavoidable part of life.
15) Fast Food Restaurants Have More Bacteria in Their Ice than in Their
Toilet Water!
Twelve-year-old science student Jasmine Roberts conducted a scientific
experiment for a school project which tested the ice machines at five fast
food restaurants for bacteria. She used the results of the testing and compared
it with the testing results for the toilet water at the southern Florida sites.

By Bryan Allison
via Wikimedia Commons
Results form the testing showed that 70% of the time, the ice had more
bacteria
than toilet water. In some of the studies' more horrific cases, beverage ice
even tested positive for E.coli bacteria.

The toilet water was apparently cleaner because that water source comes from
reasonably sanitized city water, and the toilets routinely cleaned by employees. The ice machines were
found to be cleaned less often than the toilets at many fast food locations.
14) Unwashed Jeans Have the Same Amount of Bacteria on Them after 15 Months
As They Do after 13 Days!
In 2011, Canadian college student, Josh Le embarked on a curious scientific
experiment. During the course of his studies, he met a professor who specialized
in the research of bacteria and their effect on textiles. Intrigued by this
unique area of scientific study, Le approached the professor and proposed a test
– one that would involve Le wearing a pair of jeans for 15 months without
washing the garment.

The purpose of the test was to determine just how much bacteria would
accumulate over the period. The results of this evaluation were compared with
wearing the jeans for a much shorter span of time, or 13 days – the average
amount of time most people wear their jeans before washing them.
Although he never washed the jeans, Le did make a number of attempts to keep
the jeans somewhat clean. For instance, he always had a paper towel on hand to
remove any stains from the jeans. He would also air the jeans out after wearing
them. Furthermore, he stored the jeans in his freezer overnight if they ever
started to smell. Basically, he did everything to keep the jeans “clean” short
of actually washing them.

At the end of the experiment, Le and the professor tested just how much
bacteria were on the jeans. Le then washed the jeans before wearing them for 13
days.
The experiment revealed that the amount of bacteria living in the jean
material was about the same regardless of the amount of time that the jeans were
worn.
13) The Scent of Rainwater is Caused by Bacteria
There are good bacteria and there are bad bacteria. And, then there are
“pleasant-scented” bacteria. Many people love the smell of rain, especially when
it wafts through the air after a long period of sun and heat. The scent or
petrichor results from the collection of streptomyces, or bacteria living in the
ground. The micorganisms activate the production of the chemical, geosmin, which
manufactures the smell.

12) Harmful Bacteria is Quickly Killed by Such Metals as Copper or Brass
If you are a germophobe and terrified of turning the knob on a door because
of bacteria, you may want to install copper and brass handles to lessen your
concerns. That’s because copper and brass are more hygienic than door handles
made of steel or aluminum. Copper and brass have antimicrobial properties, which
are known to produce an oligodynamic effect. In other words, they spread far
fewer germs than door handles made of other materials, such as steel or
aluminum.
Oligodynamic Effect Explained
In fact, one study showed that olgodynamic metal containers, made for holding
water, were effectively used in killing off salmonella microbes. Copper, brass,
and silver metals were tested against water containing the organisms. It took no
longer than 12 hours for the metals to kill the germs.
Other metals have the same kind of antimicrobial properties, including gold,
lead and bronze. However, copper and brass are by far better to use for
sanitizing purposes.
Brass Door Handles are Best for Sanitizing
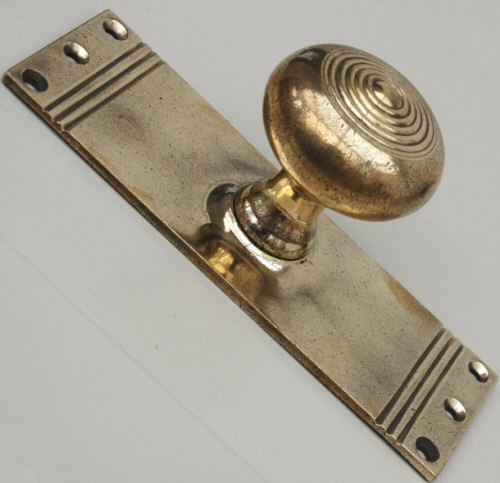

Door handles that are made entirely of copper can kill bacteria within 15
minutes while it takes brass about seven hours to eliminate germs.
11) Over 2,300 Forms of Bacteria Reside in the Belly Button
One study, conducted in 2012, which is part of a project known as “Belly
Button Biodiversity,” found that the navel holds more than 2,300 kinds of
bacteria. Sixty participants in the research study were tested, which entailed
swabbing and analyzing the volunteers’ belly buttons. Researchers discovered
1,458 types of bacteria unique to the belly button of the 2,368 kinds of
bacteria that were found.
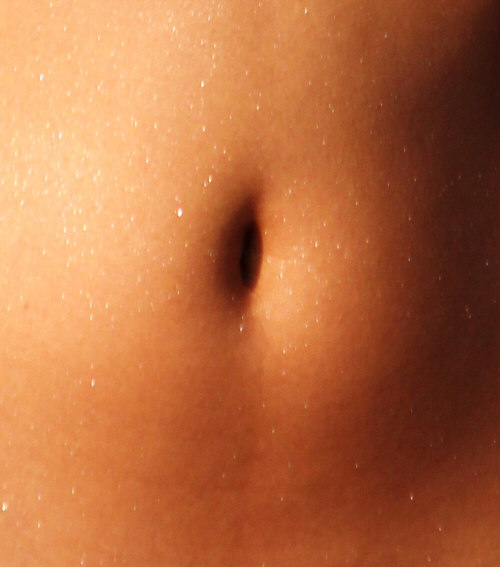
By Stinkie Pinkie
via Wikimedia Commons
Scientists contended that the large number of bacteria resulted from the
natural tendency of people to overlook cleaning the belly button when they
showered or bathed. Because the belly button serves as a point of entry in a
number of surgeries, it can also serve as a portal for harmful bacteria - a
scary thought if you are contemplating surgery.
Scanning Electron Micrograph of Escherichia coli
10) One Bacterium is Ideal for Use in Space Exploration
Among the various bacteria, the bacterium, Deinococcus radiodurans (D.
radiodurans) is by far the most impressive with respect to its ability to
survive. While other forms of bacteria can easily be killed, D. radiodurans not
only survives but also continues to thrive. In one research study, scientists
subjected the bacterium to a variety of tests in order to kill the organism.
Researchers tried bathing the microorganism in acid as well as subjecting it to
radiation or extreme temperatures. However, none of these attempts worked.

That’s because the bacterium is genetically programmed so it can repair
itself. As a result, researchers are directing their studies toward using the
resilient bacterium in the space exploration area. Because of the bacterium’s
unique ability to survive, the microorganism can be used where other life forms
might perish.
Transmission Electron Micrograph of Deinococcus Radiodurans
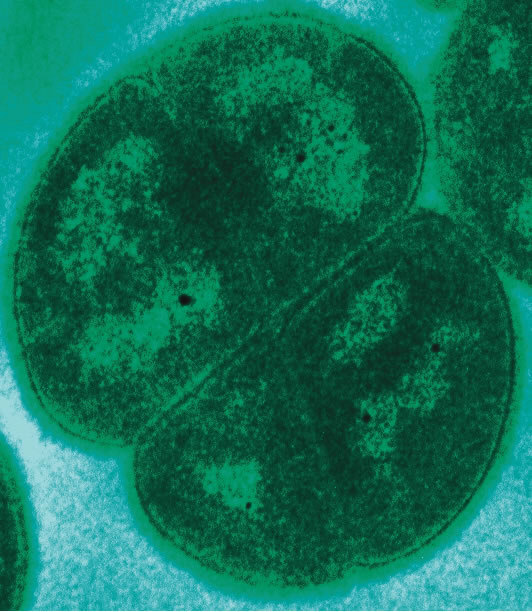
9) A Bacterium Exists that is 250 Million Years Old
In 2009, prehistoric bacteria were discovered in Carlsbad, New Mexico.
Encased in a salt crystal 1,850 feet underground, the bacteria was estimated to
be about 250 million years old. Formed during the Paleozoic Era, the ancient
organisms existed at a time when the Earth was experiencing significant losses
of life.
Gram Stain of Bacillus Species
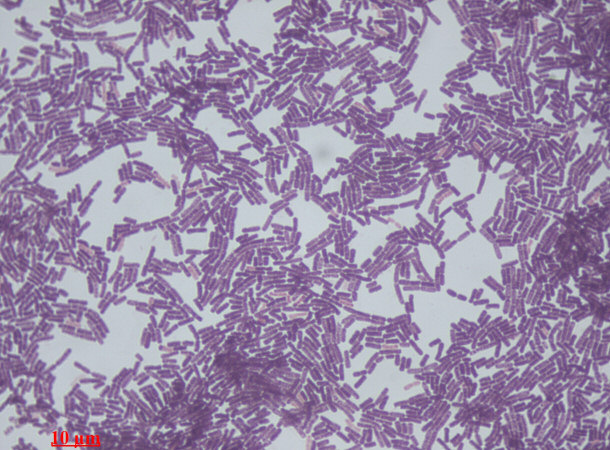
By Dr. Sahay
via Wikimedia Commons
Held in a state of suspended animation, the prehistoric bacteria survived as
spores and metabolized very little over time. DNA tests have revealed that the
prehistoric bacteria are related to the modern-day bacterium, Bacillus, which is
a type of bacteria that is commonly found in water, soil and dust.
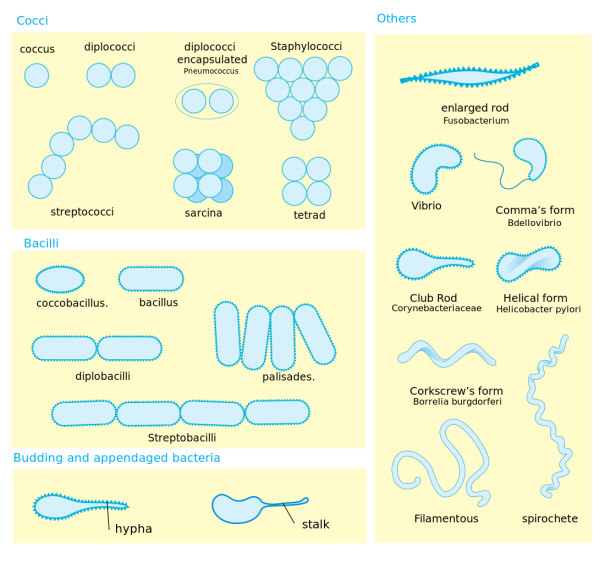
Bacterial Morphology Diagram
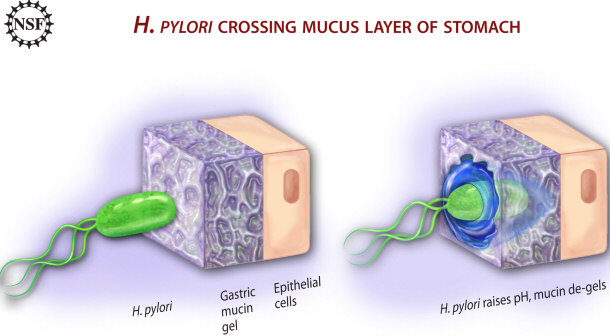
8) The H. Pylori Bacterium is the Cause for Ulcers – Not Stress
In the past, it was commonly believed that stress was the main cause of stomach
ulcers. Therefore, most of the remedies that doctors prescribed focused on
minimizing the anxiety of the sufferer. In reality, though, stomach ulcers
originate from microaerophilic bacteria which are found in the stomach.
Electron Micrograph of H. Pylori Possessing Multiple Flagella
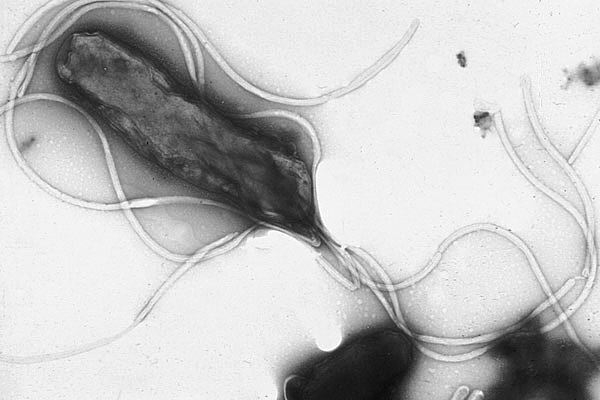
By Yutaka Tsutsumi
via Wikimedia Commons
Known as Helicobacter Pylori (H. Pylori), the bacterium is frequently found
in the upper intestinal tract and is not only responsible for ulcers but for
intestinal conditions such as stomach cancer and gastritis.
However, that being said, some people still believe that stomach ulcers form
because of stress. That myth was debunked though in the 80s. At the time, Dr.
Barry Marshall conducted an experiment that proved that the H. Pylori bacterium
was responsible for the malady. To prove his point, the researcher consumed a
sampling of the microorganism and documented the results. Eventually it was
proven as Barry did develop an ulcer. The research earned him a Nobel Price in
Medicine for his work in the discipline.
7) Bacteria Makes Up Approximately Five Pounds of a Person's Body Weight
Most people are well aware that bacteria are everywhere. In fact, regardless
of how hygienic a person is, bacteria still thrives in and around the human
body. What most people do not realize though is that this same bacteria can
impact a person's weight. On average, approximately five pounds of weight can be
attributed to bacteria.

Fortunately, most of the bacteria that adds to a person's weight is the good
form of bacteria – organisms that are essential to a person's intestinal health.
The good bacteria also protects the body from the bad kinds of bacteria.
By BruceBlaus
via Wikimedia Commons
6) The Discoverer of Penicillin Discouraged Its Use Because of Mutant
Bacteria
In 1929, British bacteriologist, Alexander Fleming (August 6, 1881 to March
11, 1955) discovered penicillin by accident. The drug, which proved to be one of
the greatest medical discoveries in history, was a concern for the scientist.
Fleming believed use of the drug would lead to it being ineffective as bacterial
mutations would eventually resist the drug.
Alexander Fleming

Fortunately, doctors ignored Fleming's warnings and, happily, penicillin
served as a stepping stone for the further development of antibiotic medicines –
medicines that are regularly used today to fight off serious infections and
build up immunity.
WWII Promotion for Penicillin Use

5) Bacteria Causes “Avatar Meat” to Glow
One special, or at least unique, kind of meat that emits a blue glow in the
dark is a pork known as “avatar meat.” Bacteria are what give the meat it
phosphorescent light. In 2011, the meat was eaten by a Chinese family, who
discovered the meat glowing in the dark.
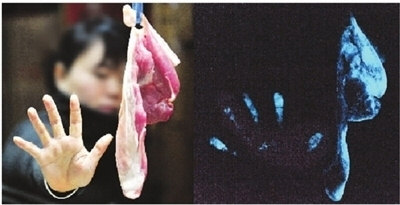
The Changsha Food Safety Commission, who investigated the report, discovered
that the blue glow resulted from a bacterial contamination. Fortunately, it was
also found that the bacteria did not produce any harmful side effects as long
the meat was completely heated and cooked.
Glowing Pork on a Plate

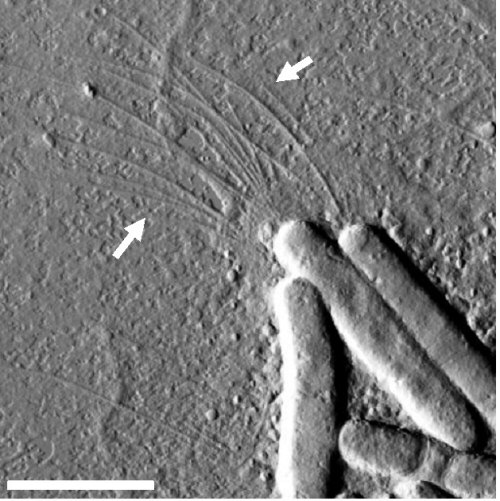
4) Bacteria Can Sling-shot Back and Forth
In 2011, researchers used a high-speed camera to capture footage of bacteria.
The cells used their natural, grappling hook-like structures, known as Type IV
pili (TFP), to sling-shot from one surface to the next. The TFP is crucial to
the movement of bacteria. Because bacteria are covered in polysaccharides (a
viscous material that significantly restricts their movements), the organisms
need TFP in able to move around.
Myxococcus Xanthus Type IV Pili
3) Bacteria Saved Lives During the Civil War
During America’s Civil War a number of wounded soldiers suffered from an
unusual phenomenon that caused their wounds to glow in the dark. The strange
phenomenon was dubbed the “Angel’s Glow."
In 1862, at the conclusion of the Battle of Shiloh, over 16,000 soldiers had
been injured. Because little was understood about infection at the time, many of
the soldiers became quite sick.
Depiction of the Battle of Shiloh

During that time, soldiers were forced to sit in the mud for hours waiting to
get treated. So, at night, many of the wounded noted that their wounds would
glow faintly in the dark. While not all of the soldiers experienced the
phenomenon, those who did had a higher survival rate.
Over a century passed before the mystery of the “Angel's Glow” was finally
solved. In 2001, scientists determined that the glow was the result of bacteria.
Specifically, it was because of the bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens (P.
luminescens).
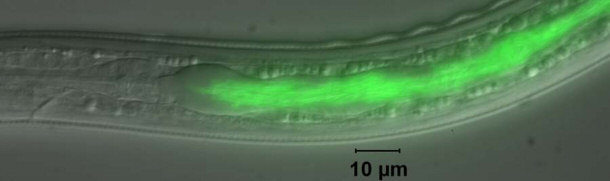
P. luminescens is a type of bacteria that flourishes in the gut of nematodes,
which track down insect larvae. The nematodes vomit the bacteria into the bodies
of the larvae. In turn, the bacteria produces chemicals that kill all the
microorganisms and larvae in the wound. Therefore, the reason for the higher
survival rate among those who experienced the Angel’s Glow was due to the P.
luminescens. The bacteria had killed the harmful organisms in the soldiers’
wounds.
2) Bacteria Results in Bio-precipitation
In 2011, researchers discovered that hailstones had large portions of
bacteria at their cores. The discovery was significant because it supported the
theory of "bio-precipitation" – the concept that suggests that bacteria play a
significant role in initiating precipitation.
The bacteria that was discovered had caused water to freeze at a relatively
warm temperature. Researchers at the American Society for Microbiology believed
that the organisms had evolved to the point where they could facilitate the
dispersal of rain, hail and snow.
Microorganisms in precipitation have been studied since the 1960s. One
particular bacterium that is commonly associated with bio-precipitation is
Pseudomonas syringae (P. syringae). The bacterium causes the formation of ice at
temperatures far higher than what is normally required.
Pseudomonas Syringae Cultures
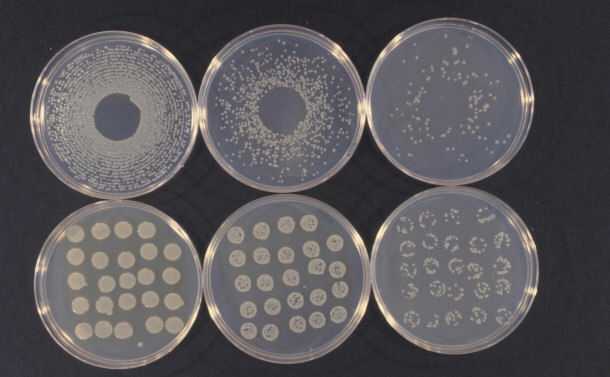
By Howard F. Schwartz
via Wikimedia Commons
P. syringae are known to accumulate on plants and then rise into the air in
updrafts. When the bacteria reach the clouds, they produce precipitation. In
2008, Dr. Brent Christner of Louisiana State University reported that his
research showed that the amount of bacteria had increased in the snow throughout
the world. Dr. Christner theorized that the process that causes P. syringae to
rise up in the clouds may be a way for nature to disseminate the bacteria.
1) Bacteria Changed the Way NASA Looks for Extraterrestrial Life
Up until the late 2000s, it was widely believed that all life in the world
was composed of six elements: hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur and
phosphorus. However, in 2010 scientist discovered the microorganism, GFAJ-1 in
Mono Lake, California. One of the building blocks used to create GFAJ-1’s
genetic material included arsenic, which is generally poisonous to most living
things on Earth.
GFAJ-1 Grown on Arsenic
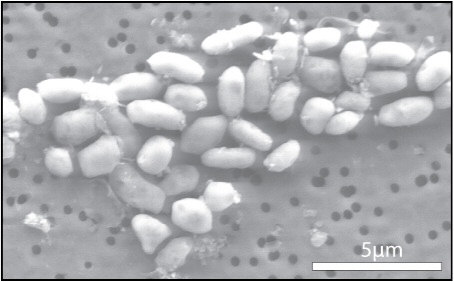
GFAJ-1 is unlike any known organism on Earth then because it utilizes arsenic
to construct its DNA. NASA scientist Felisa Wolfe-Simon and her team made the
discovery. Scientists had previously thought that every being on Earth had the
same DNA blocks.
Felisa Wolfe-Simon at the 2011 Time 100 Gala

By David Shankbone
via Wikimedia Commons
The implications of the discovery were enormous. It changed what scientists
thought they knew about the very essence of life. Furthermore, it increased the
possibility that life on other planets could be found. Because of the discovery,
scientists are now looking for new types of organisms – cells that utilize
uncommon elements. The discovery caused scientists to realize that they had been
looking for life in the wrong places all along. It also changed how NASA now
searches for extraterrestrial life in the Universe.
Conclusion
Bacteria thrive in a variety of environments. They can adapt to almost any
conditions and are found in the depths of the ocean as well as in hot springs,
in ice, and even in the stratosphere. More bacteria exist on the Earth than any
other living thing. All in all, bacteria—bad and good—are essential for the
cycle of life. Associated with germs, bacteria are organisms that are also
associated with life and health and are an incredible part of the world and
universe.
Nature
Top Lists:
15 Fascinating Facts about the Amazon Rainforest
15 Remarkable Facts About Bacteria
15 Remarkable Facts About Jellyfish
15 Little Known Facts About Elephants
15 Fascinating Facts about Earthquakes
15 Odd And Interesting Facts about Monkeys
Top 15 Myths about Snakes
Top 15 Myths about Horses
Top 15 Creepy Deep Sea Creatures
15 Unexpected Animals That Can Kill You Quickly
Top 15 Spider Myths
15 Beautiful Animals that are Now Extinct
Top 15 Most Amazing Snakes Around the World
15 Fascinating Facts about Snow
Top 15 of the World's Rarest Flowers
10 Most Emotional Animals
15 of the Most Venomous Creatures to Roam the Earth
15 Unusual Animal Defense Mechanisms
15 Unusual and Less Known Uses of Rocks
15 Unique Forest Creatures Less Known To Man
15 Interesting Facts About Time
15 Unknown Parasites You Never Knew Existed
15 Weird Trees Around The World
15 Wild Animals Deadly to Humans
15 Exotic Insects That Are Harmful & Deadly
15 Ridiculous Uses for Gold
Informational:
Preparing for a Disaster
Proof That We Are What We Are!
What is the Meaning of Life?
The Trend and Challenges Facing the Urban World
Creation Narratives and the Evolution Creationist Debate |