15 Interesting Facts About the Internet
 It's hard to imagine life without the Internet today. It connects us with
friends and business associates around the world and allows us to share
information at unprecedented speeds. In fact, without the Internet, we couldn't
spend time on Facebook, YouTube, or any other online activity we have come to
enjoy. The Internet was a huge game changer for business and personal lives.
However, most people don't know the story behind the development of the
Internet. While entire books have been dedicated to all of the stories behind
the Internet and its initiation, a few are particularly interesting. What is
strange to realize though is that at one point, none of these inventions
existed. So here is 15 Fascinating Facts About the Internet. It's hard to imagine life without the Internet today. It connects us with
friends and business associates around the world and allows us to share
information at unprecedented speeds. In fact, without the Internet, we couldn't
spend time on Facebook, YouTube, or any other online activity we have come to
enjoy. The Internet was a huge game changer for business and personal lives.
However, most people don't know the story behind the development of the
Internet. While entire books have been dedicated to all of the stories behind
the Internet and its initiation, a few are particularly interesting. What is
strange to realize though is that at one point, none of these inventions
existed. So here is 15 Fascinating Facts About the Internet.
15) Development of the Internet Started in 1960s and Continued With the
Government Until the Launch
The Internet started out as an idea to transmit data through electronic
signals. In fact, according to the History of MIT, the first decision to develop
the Internet came about when a user attempted to type in the word "login" into
the network. The network crashed because the data load related to the letter G
was too big. The tech developers realized that something had to change. This was
a sentiment shared throughout the burgeoning technological world.
Early ARPANet Teletype
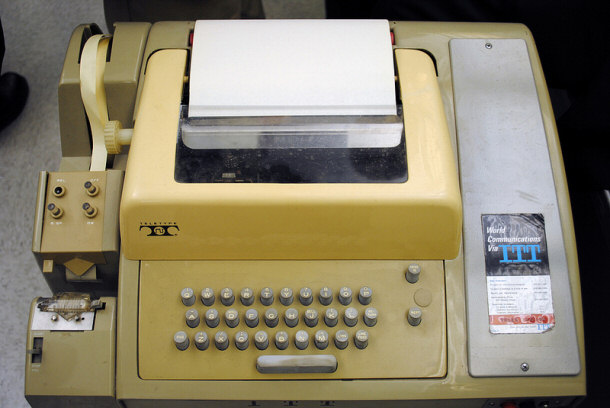

No one thought that it would be as big as it was. It was intended initially
to be nothing more than a text based service that would allow for greater
freedom and memory savings. It started out though as a computer network of
ARPANet linked computer networks throughout the United States. Several
universities and research labs participated in this. According to the OnLine Man
Computer Communication, J.C.R. Licklider's original paper in 1962, it would be
possible to connect to virtually limitless networks through gateways. He
developed key internal processes that led to the development of the initial
ARPANet and networking. Otherwise, he cautioned that it would result in a
tremendous waste of resources and space. Further developers of the ARPANet used
much of his work to develop the precursor to the Internet. His successors were
Robert Taylor and Lawrence Robert. In 1973, he returned to work with them for
another two years. The majority of the work was funded by the government or
through research facilities that received their funds from the government. NASA
played a significant role in the development of the Internet and in creating the
initial connections.
14) Timothy Berners Lee Developed the Concept of the World Wide Web
Sometimes
referred to as the Father or Inventor of the World Wide Web, Sir Timothy John Berners Lee made his initial proposals long before implementing them. At first,
most people thought his ideas were just madness. They could not imagine how they
could be brought into reality. However, his first successful proposal on the
Internet resulted in a beneficial and successful communication between a Hypertext
Transfer Protocol client and server. This created a springboard for other
developers to start building off his discovery. He termed it the worldwide web.
In fact, he called it the World Wide Web Project. He made it clear from the
beginning that he wanted this to be something that everyone would have access
to. The purpose was not to set it aside for a few individuals or just leave it
for the government.
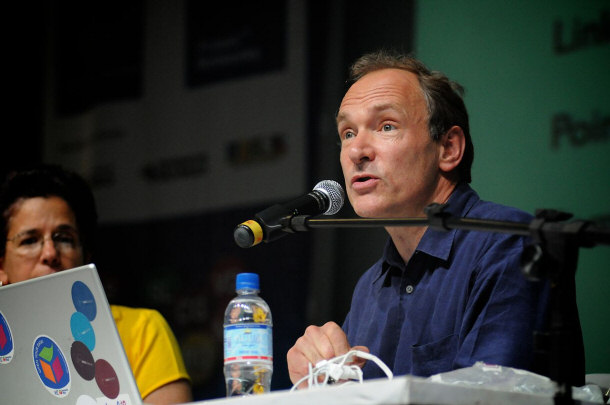

By Silvio Tanaka (originally posted to Flickr as Tim Berners-Lee) [CC-BY-2.0],
via Wikimedia Commons
Sir Timothy John Berners Lee went on to be a pivotal member in the
development of the worldwide web. According` to the "Berner Lee Biography," he
founded the W3C company at MIT. Here he worked with other companies and
professionals in the industry to develop acceptable standards and provide
recommendations. The web was still in its infancy and many of the concepts had
not yet been tested for the general public. One of the most remarkable things
though was that he chose to make these ideas and concepts available without
charge. He did not claim any patent or royalties at any point. As such, the
World Wide Web Consortium, later established, decided to follow suit. The
purpose would be to develop standards that anyone could use to participate on
the Internet. This is one of the biggest reasons that the Internet itself does
not have a charge except for the access fee that you must pay to get an Internet
connection. Had he chosen to require royalties, you would have to pay a fee
every time you accessed a web page.
All of his efforts did not go without notice. According to People Magazine,
Queen Elizabeth II knighted him for his work in the Internet and the World Wide
Web. At the 2012 Summer Olympics, he was honored as the "inventor of the world
wide web." Additionally, he has been inducted into the World Wide Web Hall of
Fame and received numerous awards for his work. Time Magazine also listed him in
the 1999 issue of 100 Most Important People of the 20th century.
13) The Internet Started Out as a Single Page
 The world's first website and web server went live Aug. 6, 1991. It was a
simple text based page and Timothy Berners Lee published it. His purpose was to
alert people to the possibility of the world wide web. He referred to it as the
World Wide Web Project. Through this, he hoped that everyone would be able to
one day contribute. This goal has, of course, been more than he ever hoped for.
This initial website was located at
//info.cern.ch/hypertext/WWW/TheProject.html. It included information on
hypertexts as well as the technical details required for creating a web page. It
even had an explanation for how you should use the Internet to create
information. It was updated regularly. The original web page was lost in the
updates, but the World Wide Consortium official website retains the 1992 copy as
part of its collection. The world's first website and web server went live Aug. 6, 1991. It was a
simple text based page and Timothy Berners Lee published it. His purpose was to
alert people to the possibility of the world wide web. He referred to it as the
World Wide Web Project. Through this, he hoped that everyone would be able to
one day contribute. This goal has, of course, been more than he ever hoped for.
This initial website was located at
//info.cern.ch/hypertext/WWW/TheProject.html. It included information on
hypertexts as well as the technical details required for creating a web page. It
even had an explanation for how you should use the Internet to create
information. It was updated regularly. The original web page was lost in the
updates, but the World Wide Consortium official website retains the 1992 copy as
part of its collection.
12) The Emoticon Was Intended to Enhance Communication from the Beginning
The use of symbols to communicate feelings and emotions is nothing new. After
all, all language is basically predicated on this. Traditional print
publications, cave paintings, hieroglyphics, and Morse code print abbreviations
are all examples of communication. The emoticons likely developed from Professor
Scott E. Fahlman. His school and computer science program had been involved in
the computer development and research program. One of his concerns was that it
would be difficult to understand the tone or meaning of a message without vocal
intonation. He then decided that certain combinations should be used to indicate
emotions. The classic :-) was his initial recommendation for general happiness
or humor while the :-( should indicate displeasure or sadness. He used it
himself among his students.

The emoticon caught on fastest among the younger Internet users. They liked
the ability to signal their emotions. However, other potential inventors have
been mentioned and it's hard to know for sure who really came up with it first.
Kevin MacKenzie is another commonly believed person to have developed the
emoticon. He too was concerned with the inability to translate the meaning of a
message without hearing the accompanying voice. His supposed emoticon was only a
dash with various symbols or letters to form the mouth. No colon was used to
indicate the eyes.
11) The First File Sharing Service Was Napster in 1998
 The first standard mp3 file was developed and perfected in 1991. This led to
an increased ability to listen to files. However, in 1998, Napster launched in
the first massive music file sharing program ever available. This forever
transformed the Internet. Ultimately Napster led to numerous lawsuits that
eventually led to shutting down Napster and its free file sharing networks.
Copyright and information protection laws changed in response to the lawsuit and
the new behavior created by the availability of Napster and other file sharing
programs. After the lawsuit, Napster was transformed and developed into an
online music store. The first standard mp3 file was developed and perfected in 1991. This led to
an increased ability to listen to files. However, in 1998, Napster launched in
the first massive music file sharing program ever available. This forever
transformed the Internet. Ultimately Napster led to numerous lawsuits that
eventually led to shutting down Napster and its free file sharing networks.
Copyright and information protection laws changed in response to the lawsuit and
the new behavior created by the availability of Napster and other file sharing
programs. After the lawsuit, Napster was transformed and developed into an
online music store.

The biggest contribution that Napster made, however, was that it led people
to realize the incredible possibilities for file sharing. It also opened up a
whole new form of piracy. The Recording Industry Association of America
developed extensive legal muscle that it has since used to enforce copyright
claims and prevent as many file transfers as possible. Hundreds of other file
sharing networks have since sprung up. The legality and illegality varies with
the organization. After Napster's foray into the field, other file sharing
networks arrived to offer movies as well as pictures and text documents for
sharing.
10) Spam First Started in 1978, Even Before the Official Internet Was Born
 The
first account of spam came about in 1978. An unknown marketing team purchased a
computer and operating system. One of the marketers decided that he needed to
send out a mass email to all 600 users and administrators. There was no official
Internet at this time. They were just using the ARPAnet and not the Internet we
know today. However, the marketer typed the addresses in such a way that all
that went through was a long list of user addresses. At the time though, it was
not known as spam. The other coworkers were annoyed with this development. The
first account of spam came about in 1978. An unknown marketing team purchased a
computer and operating system. One of the marketers decided that he needed to
send out a mass email to all 600 users and administrators. There was no official
Internet at this time. They were just using the ARPAnet and not the Internet we
know today. However, the marketer typed the addresses in such a way that all
that went through was a long list of user addresses. At the time though, it was
not known as spam. The other coworkers were annoyed with this development.
The word spam actually comes from an urban legend relating to the 1980s
multiple player online dungeon role playing games. In these games, the only
method of exploration and interaction was through texting. One of the users
decided that the experience was too boring. So he programmed the keyboard macros
to consistently type the words "SPAM SPAM SPAM SPAM SPAM" every few seconds and
send to all of the players. This resulted in the system shutting down in some
cases or freezing for a period of time. It not only detracted from game play but
caused tremendous frustration. While this has not been confirmed, this
supposedly stemmed from Monty Python's Spam Loving Vikings Sketch." Monty Python
enjoyed tremendous popularity at the time, and they never denied the connection.
The term soon caught on and was used to refer to unwanted or annoying messages
sent to people who did not want them. The term is still used to this day.
9) Many People Believed That the Internet Was Being Developed to Prevent a
Nuclear Holocaust
One of the primary technologies and theories used to connect the different
physical networks to a larger network was known as packet sharing. Paul Baran is
credited with developing studies that led to the establishment of survivable
networks throughout the military. The military’s relationship with the Internet
was given top priority. It was revolutionized by the concept that individual
segments of information could be divided into message blocks. Donald Davies
agreed that this could work, and he coined the term packet sharing. This would
allow for greater bandwidth utilization and increase response times. If
successful, it would change the entire concept for the better.
NORAD Command Center

The one downside to this was that the packet switching led to rigid routing
structures. A common problem of these was that they would fail at particular
points. Paul Baran and Tommy Krash received funds from the military to begin
focus on ways to reduce network redundancy. His initial work had focused on ways
to prevent nuclear holocaust scenarios. When people found out about his
connection to the project, it created a panic. The association led to many
concluding that a nuclear holocaust was imminent and the only salvation would be
the Internet. This of course proved to be false, but it did not keep wild rumors
from circulating for quite some time as well as some strange press for the world
wide web.
8) Multiple Networks Contributed to the Eventual Launch of the Internet
While ARPANet receives most of the attention, several other networks also contributed
to the research and scientific development of the theories. Some of them played
more minor roles while others participated in the development. Donald Davies
proposed a packet switching national data network that based itself on packet
switching. He developed the Mark I packet switch network with the National
Physical Laboratory.
The Merit Network of the Michigan Educational Research Information Triad
wanted to explore the possibilities of computer networking on a larger scale.
According to the official Merit Network site, they connected the University of
Michigan with the Wayne State University. Others soon followed. It allowed
remote submissions and terminal support as well as batch connections and
interactive file transfers.
Inspired by the ARPANet design but wanting to see what some of the
alternatives were, Louis Pouzin developed the CYCLADES. This packet switching
provided a number of networks to serve as alternative host. This package design
was the first network that made hosts responsible for data delivery. It created
greater reliability and developed some of the more common protocol mechanisms
that still provide guidance today. To this day, the host is responsible for the
data delivery, and protocols have been established to maintain those
requirements.
7) Internet is Actually Just a Simplified Term
The official term used to describe the activity was inter networking or inter
system networking. The word "Internet" first appeared on the "Internet
Transmission Control Program" booklet in December 1974. The original term
referred to what it was being used for. However, as time passed, more and more
people started referring to it simply as the Internet.
Early Interface Message Processor or "Node"

For a time, Internet and
internetworking were used interchangeably. Then in the late 1980s, the term
"Internet" became accepted as the general network name. By the 1990s, few people
even knew that there had been another reason for the name. However, developers
still referred to certain programs by their appropriate names rather than
lumping everything into one general "Internet" term pot.
6) The Internet Development Raised Concerns of a Global Digital Divide
 When
the Internet first began to become popular, a number of organizations and
interest groups had concerns. Once the fears of a nuclear holocaust had passed,
most agreed that the internet would be an invaluable addition to the way we
communicate. It seemed that it was something that the entire world should have
access to. The International Telecommunications Union describes Internet and
informational access as being as key to freedom and global rights as the right
to live free. However, technological and infrastructural divides led to a
digital divide that separated large segments of Africa and Asia, as well as
certain portions of South America from Internet access. When
the Internet first began to become popular, a number of organizations and
interest groups had concerns. Once the fears of a nuclear holocaust had passed,
most agreed that the internet would be an invaluable addition to the way we
communicate. It seemed that it was something that the entire world should have
access to. The International Telecommunications Union describes Internet and
informational access as being as key to freedom and global rights as the right
to live free. However, technological and infrastructural divides led to a
digital divide that separated large segments of Africa and Asia, as well as
certain portions of South America from Internet access.
These countries and regions were not sitting around doing nothing. According
to the New Partnership for Africa's Development website, a number of programs
were developed around the time of the
 Internet's launch to develop the necessary
technological infrastructure to support the Internet. The
United States Agency
for International Development was launched in 1996 to assist in helping to
create better lives and better economic conditions. As its official website
states, the United States Agency for International Development had significantly
more responsibilities and goals than just providing Internet access. Its purpose
included economic as well as humanitarian goals intended to benefit all nations,
particularly the third world ones. In 1996, it partnered with the Leland
Initiative, which focused on establishing Internet infrastructure in Madagascar,
Rwanda, Guinea, and Mozambique. Internet's launch to develop the necessary
technological infrastructure to support the Internet. The
United States Agency
for International Development was launched in 1996 to assist in helping to
create better lives and better economic conditions. As its official website
states, the United States Agency for International Development had significantly
more responsibilities and goals than just providing Internet access. Its purpose
included economic as well as humanitarian goals intended to benefit all nations,
particularly the third world ones. In 1996, it partnered with the Leland
Initiative, which focused on establishing Internet infrastructure in Madagascar,
Rwanda, Guinea, and Mozambique.
5) Commercial Activity Was Forbidden at First
 Initially, no Internet service providers existed. However, toward the end of
the 1980s and before the launch of the first web page, companies began forming
to provide internal services for companies and businesses. This meant that they
provided services for regional research networks as well as UUCP based email
systems. Later on in 1992, Congress passed the Scientific Advanced Technology
Act, 42 U.S.C. 1862. This permitted commercial interactivity, even if the
organization was a research laboratory or an education community. Initially, no Internet service providers existed. However, toward the end of
the 1980s and before the launch of the first web page, companies began forming
to provide internal services for companies and businesses. This meant that they
provided services for regional research networks as well as UUCP based email
systems. Later on in 1992, Congress passed the Scientific Advanced Technology
Act, 42 U.S.C. 1862. This permitted commercial interactivity, even if the
organization was a research laboratory or an education community.
This new law created a surge of Interest. Most importantly, it led to a
growth in private ownership and infrastructure. However, the irony that
developed out of this was that the Internet has no true central law. As
frequently discussed in the Journal of Internet Law, individual countries can
regulate content on their pages to a certain extent. However, no central body of
law functions or restricts access. The government's decision to step back and
allow commercial activity permitted the growth that led to the Internet becoming
such a thriving and ever growing organization.

The commercialization of
technology and inclusion of private organizations allowed the Internet to grow
as fast as it has.
4) The Term "Internet" Had to be Officially Accepted
Since the term "Internet" was just a made up word, it had to be officially
accepted. It didn't matter that by the mid 1990s, no one had ever thought of
calling it anything else. However, the Federal Networking Council met to
determine whether it was appropriate to officially call it the "internet."

This was not a small matter, since it was about far more than just whether it
should be referred to as the Internet. What was more important was that the
council came up with a definition that satisfied everyone. This was important
due to some of the different operating systems and protocols that had been
developed. Even though the Internet was quite young, it had already exploded and
grown by leaps and bounds by 1995. They hammered out an extensive definition
that most everyone could agree upon and that would provide sufficient
guidelines. After Oct. 24, 1995, this became the official name for the Internet.
The definition has not been updated since that time.
3) The Developers Believed That the Internet Would Never Stop Changing
One of the few things that all of the Internet developers firmly believed was
that once this system developed, it would never stop changing. This was
partially due to the purpose of the Internet and its predecessors. An
information transmitting system that would allow for group interaction could not
ever remain fully static.

By Dr. Avishai Teicher
via Wikimedia Commons
Most of the initial documents and research relating to
the Internet's release all inferred or specifically discussed the fact that the
Internet would change significantly in the upcoming years. The Internet followed
that pattern, expanding in ways that no one ever anticipated. Current trends
indicate that the Internet is continuing to change such as the wider and deeper
inclusion of
social media and the transformation of information packaging.
Internet specialists now work to be ahead of the curve and to anticipate what
the new trends will be.
2) Modern Email Appeared Shortly After the Advent of the Internet
|
Inventor of Email, Ray Tomlinson:

|
Inter-connective messages could be transmitted long before the Internet
became official. After all, that was part of the reason that the idea for the
Internet even started. However, electronic mail or email did not exist in the
form we understand it today. Modern email did not appear until around 1993. The
first email messaging systems actually required that both the sender and the
recipient be online in a delayed form of instant messaging. The modern email was
actually an evolution from natural messaging systems that were already being
developed.
While the first official modern email is not credited as appearing until
approximately 1993, the official father of email is a man named Ray Tomlinson.
He developed it in 1972 when he chose to include the @ symbol in the message to
indicate sending. He then developed a system to make sure that it got to the
right system. This was not, of course, widely available. His research and
development came into use primarily in 1993 and beyond.

Soon more people had
access to the Internet and wanted to use email. Before this, the military and
government related programs used this service primarily. Despite the rise of
social media options, email is still considered one of the most important
components of the Internet and to Internet communication.
1) The Theory of Internet and Computer Viruses Predated the Internet
|
Where did Internet Viruses come from?
This guy here:

|
John von Neumann published a paper known as the Theory and Organization of
Complicated Automata. This is credited as being one of the primary documents
that provided the foundation for later computer viruses and Internet viruses.
Von Neumann's actual goal in this was to develop a self-reproducing computer
program that would be beneficial, but subsequent developers found that it could
be used to corrupt data and files. According to "Computer Viruses and Data Protection ," this was quite disturbing for John von Neumann. Hackers and those
who wanted to see if they could beat the new systems or hack into the systems to
get to classified information, used his research as a guide. His work was then
expanded and developed. The first virus is supposed to have been released into
the Internet in the early 1990s. The first real anti-virus program on the other
hand, was developed in the 1980s. But anti-virus software was not released or
feasible for mass production until a few years after the first virus started
attacking the Internet. ," this was quite disturbing for John von Neumann. Hackers and those
who wanted to see if they could beat the new systems or hack into the systems to
get to classified information, used his research as a guide. His work was then
expanded and developed. The first virus is supposed to have been released into
the Internet in the early 1990s. The first real anti-virus program on the other
hand, was developed in the 1980s. But anti-virus software was not released or
feasible for mass production until a few years after the first virus started
attacking the Internet.
Internet
Top Lists:
Top 15 Myths about Google
15 Real Life Videos that Went Viral
15 Ways That Social Media is Killing You
15 Cool Facts About the Internet
15 Fascinating Facts about the Advent of Social Media
Informational:
The Basics of Cloud Computing & How it Got Started
Introduction to Web Services
Paypal - Great for Businesses and Personal Transactions
Best CPM Advertising Networks for Website Monetization
Do Websites Get Stronger As They Age?
Best Ways to Promote Your Website Online
Tips on Selling Domain Names for Maximum Profits
New Media in the 21st Century
Best PayPal Alternatives for Online Payment Options
How to Make Money Writing Reviews Online
Best Ways to Monetize a Blog or Website
Make Money from Micro Jobs Websites
What are CPC, PPC, CPM, CPI, PPI, CPA and CTR
Is Social Media or Business Blogging Right for Small Business?
How Can You Make Money Writing Online
A Guide to Using Torrents
Different Ways of Writing Articles From Home to Make Money
How Can You Help a Child or Teen with an Internet Addiction? |